
How to Start a Commercial Pumpkin Patch, What you need to know
You Want to Start a Commercial Pumpkin Patch?
Resources to help the beginning pumpkin farmer
Pumpkins are a crop that lend themselves well to small-scale and part-time farming operations, particularly for agri-entertainment operations like pumpkin patches and corn mazes. Pumpkins are seen as a profitable opportunity by many farmers. Because of this, pumpkin acreage has expanded greatly in recent years and competition in the pumpkin market is increasing. Around 1.5 billion pounds of pumpkins are produced on 75,000 acres in the United States annually
Botany: Pumpkins are a member of the cucurbitaceae family, which also includes squash, cantaloupes, cucumbers, watermelons, and gourds. Individual plants produce both male and female flowers. Fruit shape, size, and appearance (smooth or ribbed) vary, ranging from small (less than 5 pounds) to medium (12-24 pounds), and large (typically 40-60 pounds). Pumpkins originated in America.
According to the 1997 Census of Agriculture, the top ten states in pumpkin acreage are
- Illinois,
- New York,
- California,
- Pennsylvania,
- Michigan,
- Ohio,
- New Jersey,
- Texas,
- New Mexico, and
- Wisconsin.
Data on production value is sketchy, but it likely exceeds $150 million annually in the United States.
Six basic marketing alternatives are available to the pumpkin grower:
- wholesale markets,
- cooperatives,
- Contracting to Big Box stores (Wal-Mart, Kmart, Lowe's, Home Depot, etc.)
- local retailers (grocery stores),
- roadside stands, and
- pick-your-own, pumpkin patch or corn maze operations.
Some farm stands and “U-Pick” operations have developed value-added
activities such as hay rides, pony rides, corn mazes and pumpkin festivals
to boost sales. When pumpkins are
shipped to the wholesale market, they
are shipped in bulk bins or stacked loose in trailers.
In wholesale marketing, either you or a shipper can take your crop to the market. Shippers generally sell and transport pumpkins for a predetermined price. Wholesale marketing is subject to the most price fluctuations. Marketing cooperatives generally use a daily pooled cost and price, which spreads price fluctuations over all participating producers. Local retailers are another possible market, but you must take the time to contact produce managers and provide high-quality pumpkins when stores require them.
Roadside stands (either your own or another grower's) and pick-your-own operations provide opportunities to receive higher than wholesale prices for your pumpkins, but you may have some additional expenses for advertising, building and maintaining a facility, maintaining liability insurance and providing service to your customers. With pick-your-own operations, you save on harvest costs, but you must also be willing to accept some waste.
Depending on your location, processors may or may not be a marketing option. Processors are less likely to contract with small-acreage growers.
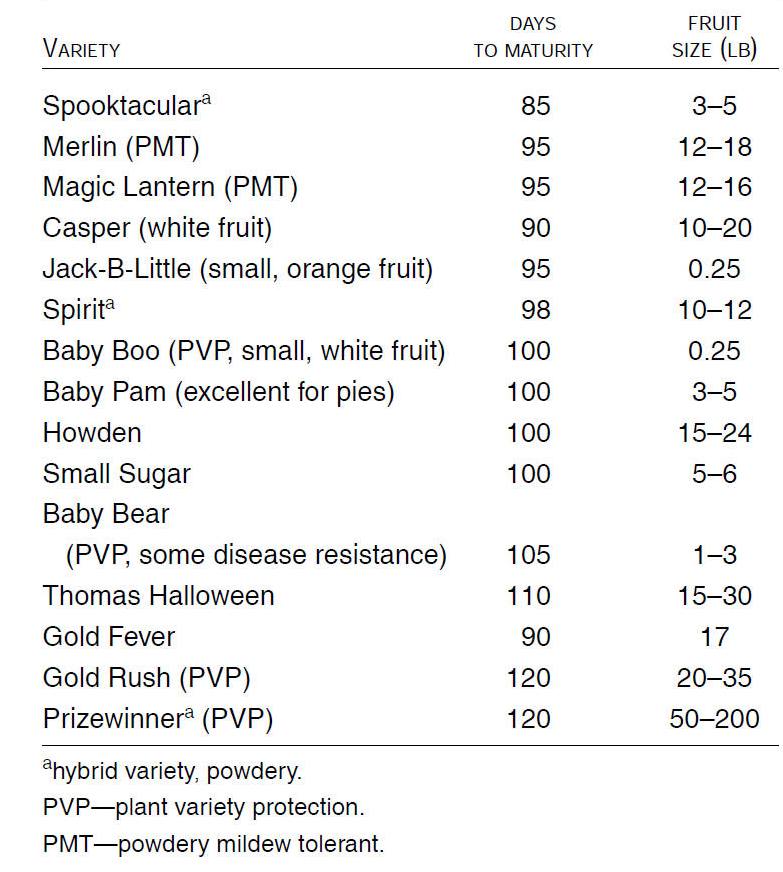
Common commercial pumpkin varieties:
Growing pumpkins
Pumpkins grow best on soils that hold water well and have good air and water filtration. If you grow pumpkins on sandy soil, irrigation is important to ensure optimum plant growth, uniform fruit set, and robust development. Soil should have a pH of 5.8 to 6.6. Pumpkins require a constant supply of moisture during the growing season. Water deficiency or stress, especially during the blossom-fruit set period, can reduce fruit size or cause blossoms and fruits to drop, resulting in reduced yields.
Pumpkins also are sensitive to cold temperatures and plants can be injured by even a slight frost. The best average temperature range during the growing season is between 65° and 95°F; temperatures above 95°F or below 50°F will slow the growth and maturation of the crop.
Budgets
PennState says the Initial resource requirements for irrigated pumpkins are:
-
Land: 1 acre
-
Labor: 19 hours per acre
-
-
- Depreciation on equipment: $300 per acre
Resources and References
Overall guides to growing pumpkins commercially
How to start a pumpkin patch or other gri-entertainment operation
- Find your county extension agent's office
- TV, Radio, Magazine and Newspaper Stories About or Including Pick-Your-Own
- Agriculture.com's guide
- Liability and insurance issues and management
- Unique Niches: Agritourism in Britain and New England (a publication)
- Commercial strawberry production guide
Pumpkin Production
- Commercial Production and Management of Pumpkins and Gourds, University of Georgia - This online publication covers all parts of successful pumpkin management and includes marketing tips.
- Grading Manual for Canned Pumpkin and Canned Squash, Ag Marketing Service, 1957 - This document details how pumpkins are processed.
- A Halloween Pumpkin Primer, The State Journal-Register, 2009 - Illinois leads the United States in pumpkin production and processing.
- A Halloween Tradition, AgSelect.com, 2001 - This site provides a general overview of pumpkins, production and marketing.
- Organic Pumpkin and Winter Squash Production, Appropriate Technology Transfer for Rural Areas (ATTRA), NCAT, 2003 - This document covers production, weed and pest management, harvesting and marketing.
- Pumpkin Butter and Mashed or Pureed Squashes, University of Georgia, 1997 - This one-page document reviews safety regarding canned pumpkin products.
- Pumpkin Nook - This Web site calls itself the "Internet shrine and library for pumpkins." It includes information on growing, holiday ideas and educational material.
- Pumpkin Production Guide, Natural Resource, Agriculture, and Engineering Service, 2003 - This 152-page guide covers the basics to cutting-edge research. It includes sample budgets and marketing ideas. It is available for purchase.
- Pumpkins, Vegetables and Melons Outlook, Economic Research Service (ERS), USDA, 2007.
- Pumpkins & More, University of Illinois - This site is completely devoted to pumpkins. It includes sections on growing, selection and uses, varieties and festival ideas.
- Pumpkins and Squash, Vegetable Research and Information Center, University of California Cooperative Extension - This resource site has links to summer and winter squash and pumpkin production.
- Pumpkins, Commercial Vegetable Production, Kansas State University - This document outlines commercial pumpkin production for Kansas. It includes production costs and direct marketing ideas.
- Vegetables and Melons, ERS, USDA - This government portal provides general information and statistics on the U.S. vegetable and melon industries.
Crates and bins to ship your pumpkins. We have no affiliation with any of these.
Fertilizer and Pest management
- Water Management and crop enhancements - M&D Enterprises has a water management program which they say will increase the efficiency of water. Reduce runoff which will reduce erosion, increase effectiveness of herbicides, pesticides, and fertilizers, elimination of dry spots on lawns, pastures, crop fields, and alfalfa. Seed treatment for germination and root growth. A liquid micronutritional fertilizer supplement to help maximize crop yield.
Businesses/Case Studies
- Arata Pumpkin Farm, Half Moon Bay, California - This farm claims to be the oldest working pumpkin farm in San Mateo County. Pumpkins have been grown since 1932. The Arata farm specializes in hosting school groups. It also distributes pumpkins nationwide.
- Bengtson's Pumpkin Farm, Lockport, Illinois - Bengtson's, a working pumpkin farm, offers a variety of activities for families, including a haunted and fun barn, pumpkin launcher and racing pigs.
- County Line Orchard, Ag Marketing Resource Center, 2002 - Located in Hobart, Indiana, County Line Orchard is operated by the McAfees, a fifth-generation farm family. The orchard is a pumpkin and you-pick apple farm that specializes in agritourism. The farm hosts students and teachers for educational tours. About half of the family's total business comes from pumpkin sales and apple and cider sales.
- Happy Apple Farm, Penrose, Colorado - This farm offers more than just apples. The you-pick pumpkin patch becomes haunted during October. The farm hosts Halloween activities that include each guest receiving a pumpkin, candy and a “death ride to lighted pumpkin field.” Visitors are encouraged to dress in costumes.
- Kathy's Pumpkin Patch, Donnellson, Iowa - The pumpkin patch is part of a third-generation crop farm located in southeast Iowa. The farm grows about 30 acres of pumpkins, squash and fall ornamentals and sells them at their roadside stand. Kathy's Pumpkin Patch also hosts fall activities and events through Halloween.
- Milky Way Farm, Chester Springs, Pennsylvania - The family-owned and -operated dairy farm offers birthday parties and private and school group tours. During October, the farm hosts a you-pick pumpkin patch. About 25,000 pumpkins are grown on 10 acres.
- Nordic Ridge Gardens, Calumet, Minnesota - This former dairy farm promotes educational school field trips during September and October. In addition to thousands of pumpkins, the farm raises squash, gourds and strawberries.
- Swan Pumpkin Farm, Franksville, Wisconsin - This farm in Racine County features many activities and tours during harvest and Halloween, such as pumpkin bowling, a corn maze and a haunted house.
- Walters' Pumpkin Patch, Burns, Kansas - This pumpkin patch started out as a farming and ranching business for Carroll and Becky Walters. In 1998, the Walters decided to grow pumpkins as a business, and Walters' Pumpkin Patch began to take shape.
Agencies
- Data Resources - Includes census of agriculture, USDA marketing and research sites and the National Ag Library.
- National Agricultural Statistics Service State Offices - Find specific production and agricultural statistics for each of the 50 states.
- The National Organic Program - State Contacts - Contacts for state offices and directors of the USDA organic program.
Halloween Costumes
Here are some of the most popular Halloween costumes for children this year. For more choices, see our Halloween costumes pages.
- Inflatable Riding Dinosaur Costume for Adults - everyone LOVES this costume. It's a hit where ever you go!
- Harry Potter Costume Kids Plush Robe - With a hood, one for each house, Gryffindor, Hufflepuff, Slytherin, Ravenclaw, Hogwarts
- Wizard Robe Cloak Halloween costume for Kids
- Girl's Sparkle Princess Costume - In pink, for small girls
- Sew your own Halloween Costumes with Patterns from the Singer Sewing Reference Library
- Pizza Costume for Kids - A giant slice of pizza Halloween Costume for Children and Teens
- Easy Halloween Costumes for Children - Miniature patterns for 3 to 12 year old children, just enlarge and use
Find Related Information and Resources Here!
Here's the quick list to related farms for PYO, Honey, Pumpkins, Christmas trees, etc.:
You may find these websites useful!
- Local pick your own farms for apples, strawberries, raspberries, corn, tomatoes, etcr
- Farm markets and roadside stands
- Local Honey Finder
- Children's consignment sales
- Local Meat, Milk and Eggs
- Christmas Tree Farms and lots
- Road tripping and camping tips, tricks and How-to's
- Fun Factory Tours
- Venues for you event: Farms, Wineries, Orchards for your event, wedding or party
- Easter egg hunts
- Festivals: Fruit and vegetable festivals
- Winery tours and wine tastings
- Horses: rides, stables, lessons, trails
- Maple Syrup farms and sugarworks
- Bed and Breakfasts on Farms, Wineries, Ranches and Orchards
- Zombie Paintball venues
- Environmental resources
- Consumer fraud information
- Wholesale food sources
- Resources for Farmers
- Pumpkin patches
- Corn mazes
Water bath canning kit - 8 Piece Enamelware Pot with Canning kit and Rack. Canning Supplies Starter Kit
Double Donut Pumpkin Spice Coffee Pods, Single Serve Flavored Coffee for Keurig K Cups Machines,
Pumpkin Spice - Organic, 1.94-Ounce Jar, Nutmeg, Cloves, Ginger & Cinnamon, Enhances Tea, Seasoning, Kosher
Maud's Pumpkin Spice Instant Latte - 16 count Packets, Love Me Some Pumpkin Spice Latte
Pumpkin Pie Spice Blend Extract,McCormick Pure
Don't miss our page of costumes, ready made and ones you can make yourself!
And here's a book of 130 pumpkin carving stencils!
Pumpkin Carving stencils book - Over 130 Halloween jack olantern pumpkin designs. Including Witches, Cats, skulls, bats, ghosts, and so much more
More carving kits and stencils are here!
Find Other types of farms:
- Pick Your Own apples
- Christmas Tree Farms and lots
- Farm markets and roadside stands
- Local Honey
- Local Meat, Milk and Eggs
- Road trip and camping
Get the
most recent version of
the Ball Blue Book
Click here to get Halloween Costumes delivered - fast, great prices!
Click here to get Halloween Costumes delivered - fast, great prices!
Find Other types of farms:
- Pick Your Own apples
- Christmas Tree Farms and lots
- Farm markets and roadside stands
- Local Honey
- Local Meat, Milk and Eggs
- Road trip and camping
Get the
most recent version of
the Ball Blue Book